-
LIGHTING UP THE
OPERATING ROOM![]()
Lighting up the Operating Room: Overview of Surgical Lights
Surgical lights are an essential component of any modern operating room. These lights provide surgeons with the illumination they need to perform delicate and intricate procedures with precision and accuracy. In this article, we will explore what surgical lights are, how they work, and why they are so important in modern medicine.
What Are Surgical Lights?
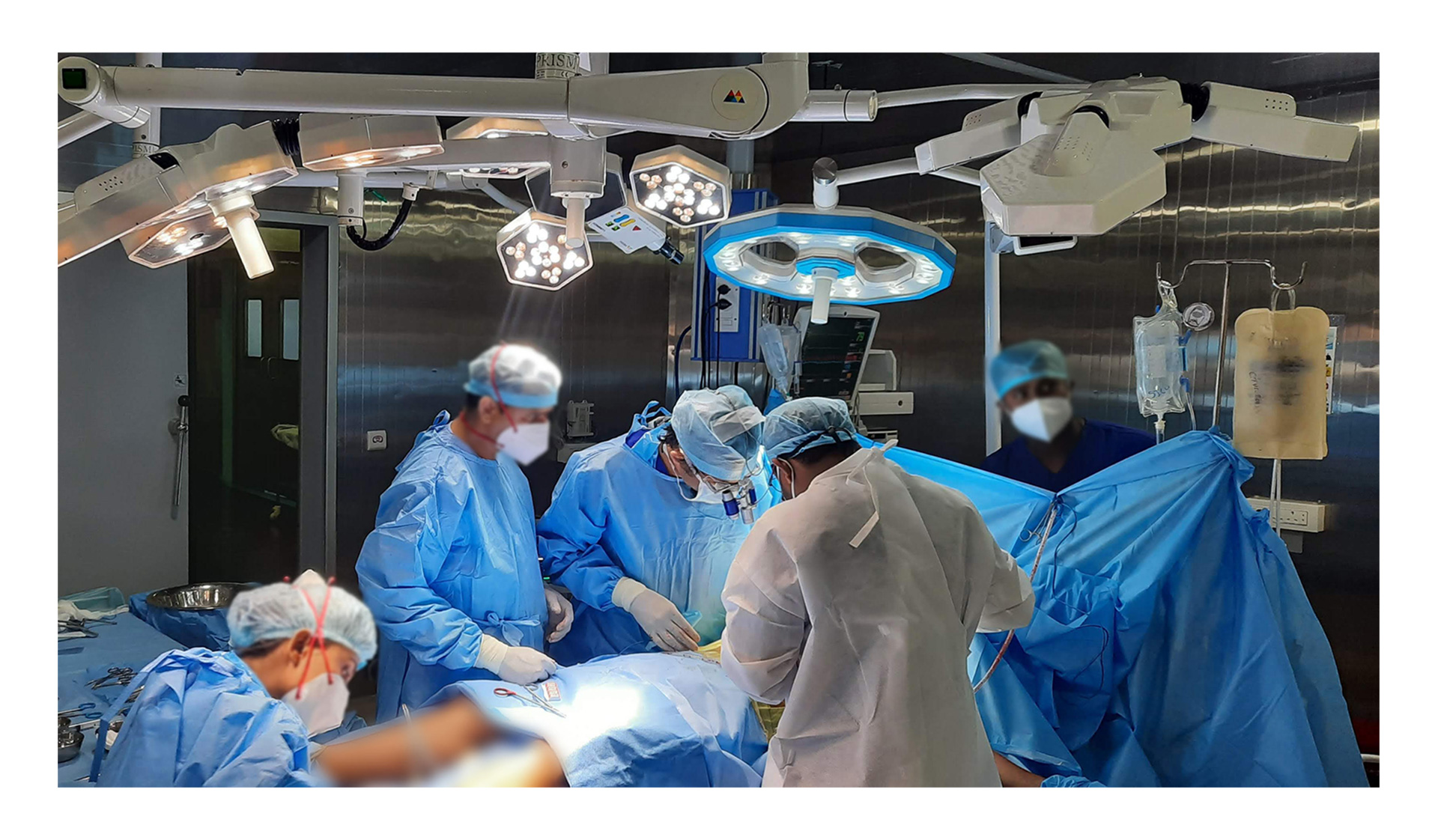
Surgical lights are specialized lights that are designed to provide bright and focused illumination during surgical procedures. Surgical lights can be used in a wide range of surgical procedures, including general surgery, neurosurgery, orthopedics, and many others.
Surgical lights typically consist of multiple light sources, often with LED or halogen bulbs, that are arranged in a way to minimize shadows and provide uniform illumination across the surgical field. The surgical lights are typically mounted on a movable arm or ceiling mount, allowing them to be positioned precisely over the area of the patient where the surgery is being performed.
One of the key features of surgical lights is their ability to provide a high degree of control over the direction and intensity of the light. This is particularly important during complex procedures where the surgeon needs to be able to see very fine details. Surgical lights can be adjusted to provide different levels of brightness, and they can also be angled and positioned to provide the best possible illumination for the surgeon. Additionally, surgical lights often have features to minimize heat generation, as well as to reduce the transmission of bacteria and other contaminants. Some surgical lights are also designed to be compatible with video recording equipment, allowing the surgery to be recorded for later analysis or teaching purposes.
History Of Surgical Lights
The history of surgical lights can be traced back to the late 19th century, when electric lighting was first introduced. Early surgical lights consisted of a single bulb mounted on a stand, which could be positioned over the patient's body to provide illumination during surgery.
However, these early lights were not very effective, as they produced a lot of heat and often cast shadows over the surgical field, making it difficult for surgeons to see what they were doing. It was not until the 1920s that the first major innovation in surgical lighting occurred, with the introduction of the "operating room light" by the German company Siemens.
The Siemens operating room lamp was a major improvement over previous designs, as it consisted of multiple bulbs arranged in a circular pattern, which provided more even illumination across the surgical field. It also had a movable arm that allowed it to be positioned more precisely over the patient.
In the following decades, other companies developed their own surgical lighting systems, with advances in technology allowing for brighter, cooler, and more efficient lighting. In the 1950s and 1960s, the introduction of halogen bulbs and fiber optic technology led to further improvements in surgical lighting.
Today, surgical lights are an essential component of any modern operating room, and continue to be refined and improved upon with advances in LED lighting, wireless controls, and other technologies.
Why Are Surgical Lights Important?
Surgical lights are critical to the success of modern surgical procedures. Without proper illumination, surgeons would not be able to perform delicate and intricate procedures with the precision and accuracy that is required. Good illumination is also important for patient safety, as it helps to reduce the risk of complications during surgery.
In addition to their role in providing illumination, surgical lights are also important for creating a comfortable and productive working environment for the surgical team. These lights are designed to reduce glare and shadows, which can be distracting and tiring for surgeons and other medical professionals. By providing a clear and consistent source of illumination, surgical lights help to improve the efficiency and accuracy of surgical procedures.
Requirement for Surgical Lights
Surgical lights are an essential component of any modern operating room, and there are a number of requirements that must be met in order to ensure that they are effective and safe for use. Here are some of the key requirements for surgical lights:
Illumination:
Surgical lights must provide bright, uniform illumination of the surgical field in order to allow the surgical team to see what they are doing. The amount of illumination required will depend on the specific procedure being performed, but generally ranges from 10,000 to 160,000 lux.
Color temperature:
The color temperature of surgical lights should be in the range of 4,500 to 6,500 Kelvin in order to provide a natural, white light that accurately represents the color of tissues and organs.
Color rendering index:
The color rendering index (CRI) is an important factor to consider when choosing surgical lights. CRI refers to a light's ability to accurately represent colors compared to natural daylight. The CRI scale ranges from 0 to 100, with a CRI of 100 indicating that colors are rendered accurately and vividly.
Shadow control:
Surgical lights should be designed to minimize shadows and eliminate glare, which can make it difficult for the surgical team to see what they are doing.
Heat management:
Surgical lights should be designed to produce minimal heat in order to avoid tissue damage or burns during surgery. This is particularly important in procedures that involve lasers or other sources of heat.
Sterility:
Surgical lights must be designed to be easily cleaned and disinfected in order to maintain a sterile environment in the operating room.
Durability:
Surgical lights must be built to withstand frequent use and harsh operating room conditions, such as exposure to cleaning agents and bodily fluids.
Choosing the Lighting for Procedures
Choosing the Lighting for Procedures Choosing the appropriate lighting for surgical procedures is an important consideration, as it can help to ensure that the surgical team has a clear view of the surgical field, minimizing the risk of errors or complications. Here are some factors to consider when choosing lighting for different procedures:
Procedure type:
The type of procedure being performed will have a significant impact on the lighting requirements. For example, procedures that involve delicate tissues or organs may require more focused lighting, while procedures that involve larger surgical sites may require more diffuse lighting.
Patient positioning:
The position of the patient during the procedure will also impact the lighting requirements. For example, if the patient is in a prone position, the lighting may need to be adjusted to ensure that the surgical field is adequately illuminated.
Surgeon preferences:
Surgeons may have their own preferences for lighting intensity, color temperature, and other factors. It is important to consult with the surgeon to ensure that the lighting is tailored to their specific needs.
Equipment compatibility:
The lighting system must be compatible with other equipment being used during the procedure, such as imaging equipment or laser systems.
Safety considerations:
The lighting system must be designed to minimize the risk of tissue damage or burns during the procedure. This may involve using LED lights that produce less heat, or positioning the lights to avoid direct contact with the patient.
Sterilization requirements:
The lighting system must be designed to be easily cleaned and disinfected in order to maintain a sterile environment in the operating room.
Overall, choosing the appropriate lighting for surgical procedures requires careful consideration of a variety of factors. It is important to consult with the surgical team and carefully evaluate the lighting requirements in order to ensure that the procedure is performed safely and effectively.
Surgical Lighting Accessories
There are a variety of accessories that can be used with surgical lighting systems to enhance their functionality and performance. Here are some common surgical lighting accessories:
Sterilizable handles:
Sterilizable handles can be attached to surgical lights in order to allow for easy adjustment of the lighting angle and position during the procedure. These handles can be sterilized and reused, minimizing the risk of contamination.
Light filters:
Light filters can be attached to surgical lights in order to adjust the color temperature of the light or reduce glare. For example, blue light filters can be used during neurosurgery to enhance visualization of blood vessels and other structures.
Wall-mounted controls:
Wall-mounted controls can be installed in the operating room in order to allow for easy adjustment of the lighting system during the procedure. These controls can be programmed to adjust the intensity, color temperature, and other settings of the lights.
Remote controls:
Some surgical lighting systems may include remote controls that allow the surgeon or surgical team to adjust the lighting without needing to physically touch the light itself. This can be particularly useful in procedures where sterility is a concern.
Camera systems:
Camera systems can be integrated with surgical lighting systems in order to provide clear, high-quality video of the surgical field. These systems can be used for live streaming, documentation, or training purposes.
Mobile stands:
Mobile stands can be used to provide additional flexibility and mobility to surgical lighting systems. These stands can be easily moved around the operating room to provide optimal lighting for different procedures.
Overall, surgical lighting accessories can enhance the functionality and performance of surgical lighting systems, providing greater flexibility, control, and visualization for surgical teams.
Summary
Surgical lights play a crucial role in providing optimal visibility during medical procedures. Selecting the right lighting system has always been a challenging process as it is critical for ensuring patient safety and staff comfort.
Opting for an inferior lighting system can have negative consequences for both the perioperative team and clinical outcomes for patients. This is due to the fact that inadequate lighting can create safety hazards and heighten the possibility of injuries, especially if the object's position, shape, or speed is misjudged. It can also affect the accuracy and precision of the work being performed, and excessive or insufficient lighting may cause eye strain and discomfort for staff.
Surgical lighting is a complex and advanced technology that is frequently tailored to suit each operating room's unique requirements. As a result, acquiring this equipment is a multi-stage process that guarantees that the correct equipment is procured to perform safe and effective procedures. The latest standard in surgical lighting can aid organizations in achieving this objective while also avoiding recognized challenges.